Strategy as Human Survival Instinct
Strategy is deeply embedded in human evolution and survival. Our ancestors met astonishing challenges in their surroundings and were susceptible to disease, injury, and predators. Environmental change — one of the ongoing challenges to survival — created both risks and opportunities in the lives of early humans.
The term “Strategy” found its definition in biological terms in Charles Darwin’s work On the Origin of Species (1859) and an economic expression in Herbert Spencer’s Principles of Biology (1864) that is based on the Principles of ‘Survival of the Fittest’. Economies in the age of Industrialization in the 18th and 19th Centuries were influenced by the Darwinian Theories and formalized by Business Schools around 1960, misinterpreting them:
1️⃣ Domination over Adaptation.
2️⃣ Ignoring the cooperative elements essential for complex system success.
3️⃣ Destructive rather than generative Competitive Dynamics.
The evolution from “survival of the fittest” to thriving strategies represents one of the most profound shifts in strategic thinking, moving from zero-sum competition to positive-sum value creation. This transformation fundamentally redefines how organizations approach Strategy, Innovation, and Growth through Learning and Adapting to New Paradigms.
From Competition to Collaboration:
👉 Ecosystem Thinking: Creating value through network effects and partnerships.
👉 Symbiotic Relationships: Mutual benefit rather than zero-sum competition.
👉 Collective Intelligence: Leveraging diverse Capabilities (Data, Talent, Resources / Materials / Energy), Financial Capital and Digital (Public & Private) Infrastructure across networks.
Regenerative Value: Creating value that benefits all ecosystem participants.
From Survival to Thriving:
👉 Proactive Environment Shaping: Creating conditions for collective success.
👉 Innovation acceleration: Faster breakthrough development through collaboration
👉 Sustainable Advantage: Digital Systems that are Device, Channel and Medium Independent.
👉 Customer Universe Alignment: Including Clients, Employees, Process Stakeholders, Shareholders, Business Partners, Vendors, Society (In which the business operates) and Technology (Devices, IOT, Sensors, Scanners & Wearables).
Strategic Thinking has and will always be a factor of using the Technology and Tools available to devise a Progressive Path for Action. Enterprise delivers a Solution while Business delivers Products and Services. The Value Delivered is a derivative, from enterprise to business.
Strategic Inflection Point (SIP)
The transition from the industrial to the intelligent era represents one of the most profound strategic inflection points in human history. This shift demands a fundamental reimagining of how strategy is conceived, developed, and executed.
Efficacy and efficiency are often used interchangeably, but they represent distinct concepts crucial for success in any field, from business to personal development.
🚀 Efficacy (or Effectiveness) refers to doing the right things — achieving the desired outcome, goal, or result. It’s about Impact and whether the actions lead to the intended effect.
🚀 Efficiency refers to doing things right — optimizing the use of resources (time, money, effort, personnel) to achieve a result with minimal waste. It’s about the process and maximizing output relative to input.
While both are important for overall success, prioritizing efficacy means focusing on achieving the right results, even if it means initially expending more resources. Once efficacy is established, efficiency can then be pursued to optimize the process.
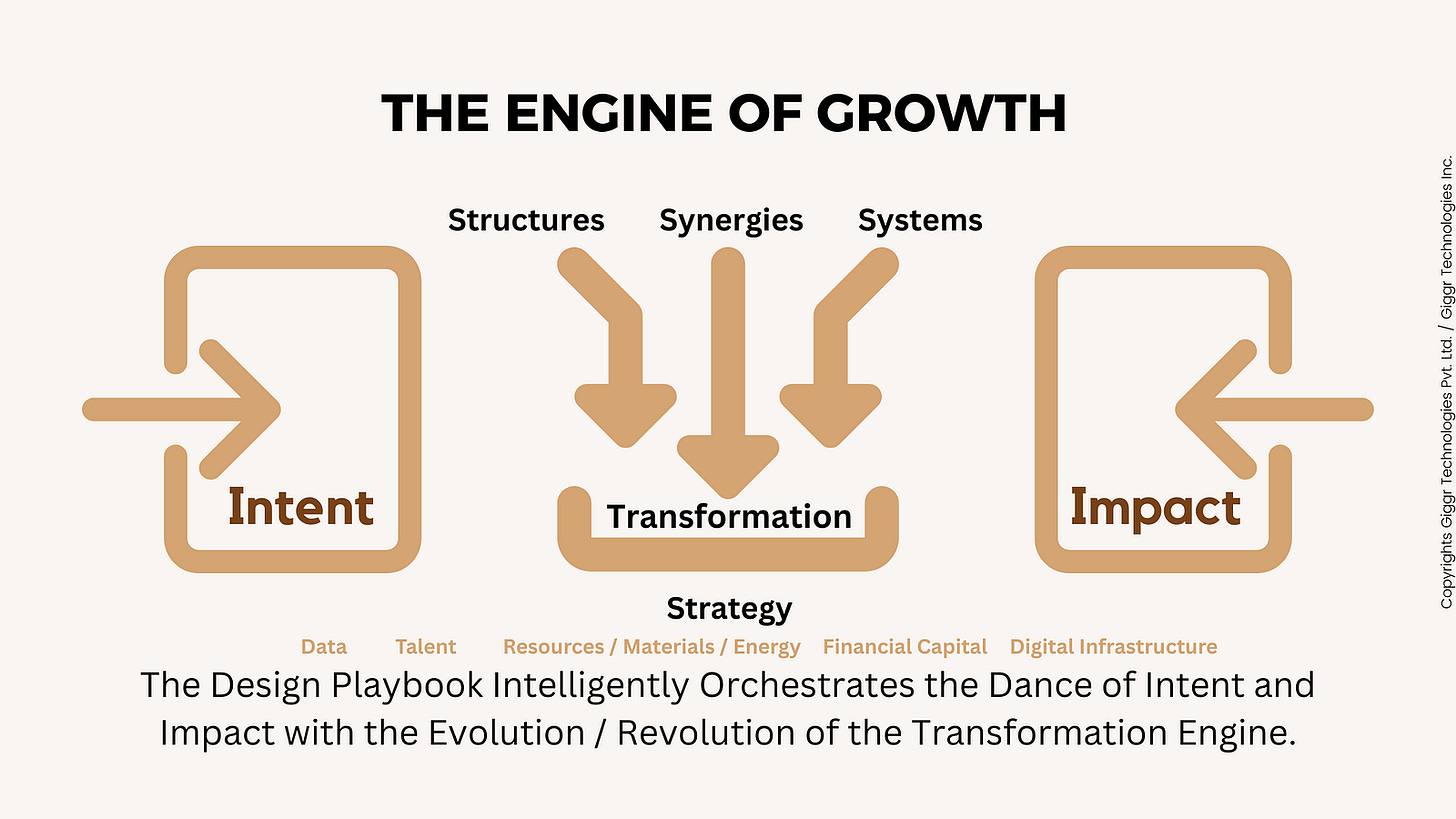
Design Playbook
A Design Playbook is the most critical tool that every Startup, Fortune 500, Multinational Conglomerate and / MSMEs aiming to consistently bridge the gap between their strategic intent and tangible impact. Choreographing the “dance of design with strategy,” ensuring every step is purposeful and contributes to the overall performance.
Key Elements of an Effective Design Playbook:
To effectively choreograph the journey from intent to impact, a design playbook should typically include:
1️⃣ Design Principles & Philosophy: The core beliefs and guiding values that inform all design decisions. These should be rooted in the enterprise’s Mission and Vision.
2️⃣ Leadership & Culture: Aspirational, Agile, Anticipating, Authentic, and Able.
3️⃣ Governance & Roles: Clear definitions of Processes, Roles, Data, Logic & Rules, and escalation paths within the design ecosystem.
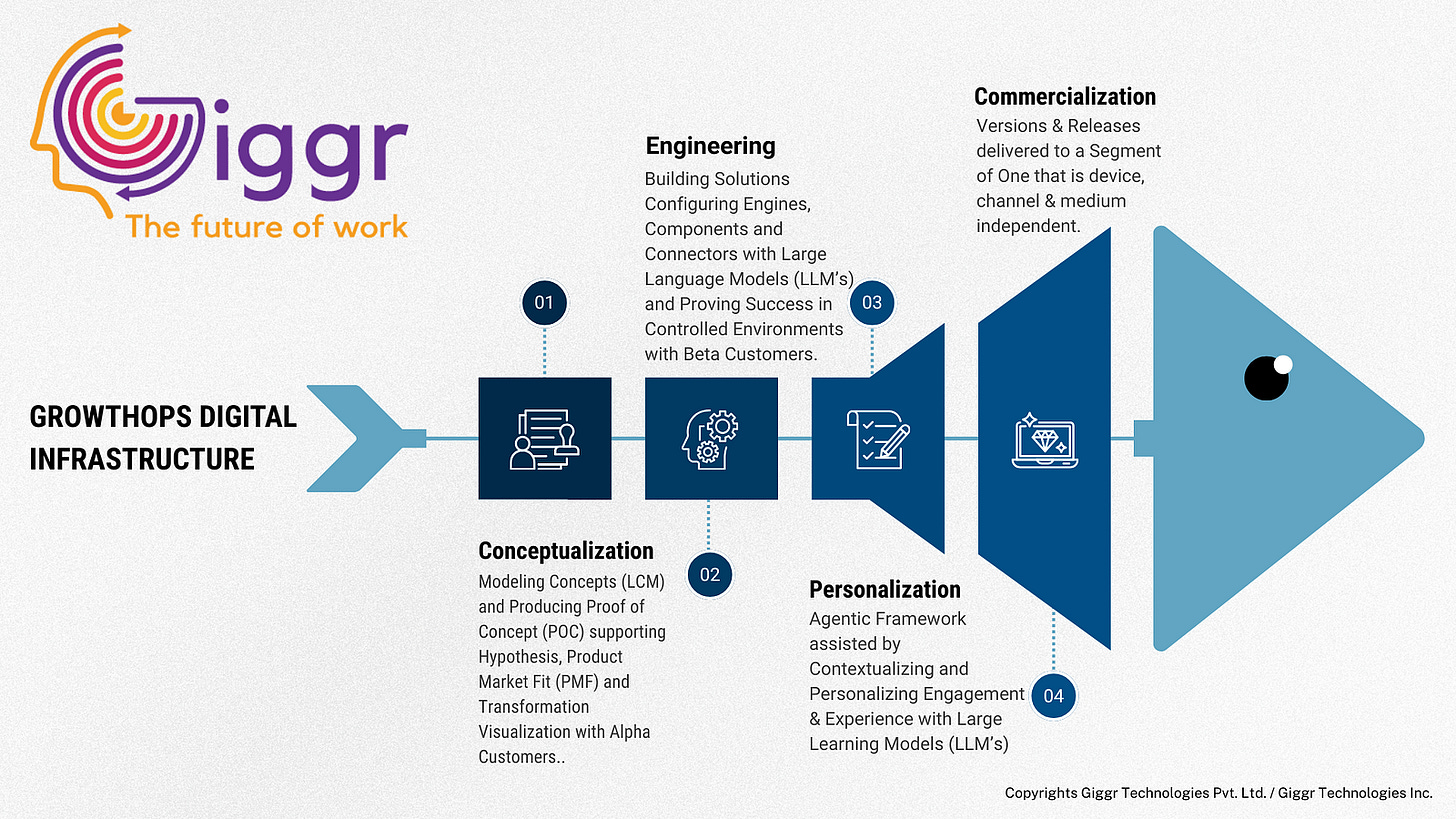
4️⃣ Strategic Framework Integration: How Design Priorities transports Intellectual Property (IP) from Conceptualization (Models) to Creation (Engineering Engines, Components & Connectors for Solutions), Contextualization (Profiling, Personalization & Preferentiation), and Commercialization (Versions & Releases to a Segment of One).
5️⃣ Measurement & Evaluation Frameworks: How the success of design initiatives is measured against business objectives and user outcomes, enabling continuous learning and improvement. Advancing Proof of Concepts (POC) to Proof of Success (POS / Prototypes) to Proof of Realization (POR).
6️⃣ User Research & Empathy Methods: A catalog of techniques for understanding user needs, behaviors, and pain points, engaging Alpha, Beta and Theta Customers (e.g., user interviews, surveys, usability testing, persona development).
7️⃣ Design System & Brand Guidelines: Components, patterns, and visual/verbal guidelines that ensure consistency, efficiency, and brand coherence across all touchpoints.
8️⃣ Collaboration & Communication Models: Guidelines for how Role Driven Digital Identities interact with one another across an Ecosystem to assure Data Continuum (Creation to Consumption).
9️⃣ Tooling & Technology Stack: Recommended software, hardware, embedded ware, Virtual Ware, Platforms, and Tools that facilitate the design and Implementation process.
Strategy Value Creation Journey
The evolution reveals several critical insights:
📍From Planning to Dynamic Capabilities: Strategy moved from rigid planning to adaptive capabilities that create value through continuous evolution.
📍From Internal Focus to Ecosystem Thinking: Value creation expanded from internal operations to understanding entire value ecosystems.
📍From Shareholder to Customer Universe: The Shift from DevOps to GrowthOps needs a Digital Infrastructure.
📍 Transversal Value: The definition of value broadened from purely financial returns to Benefits for the Customer Universe, including Functional, Lifetime, Emotional, Brand, and Economic Value.
📍From Analysis to Synthesis: Modern strategy integrates analytical rigor with Data Synthesis for breakthrough Value Creation.
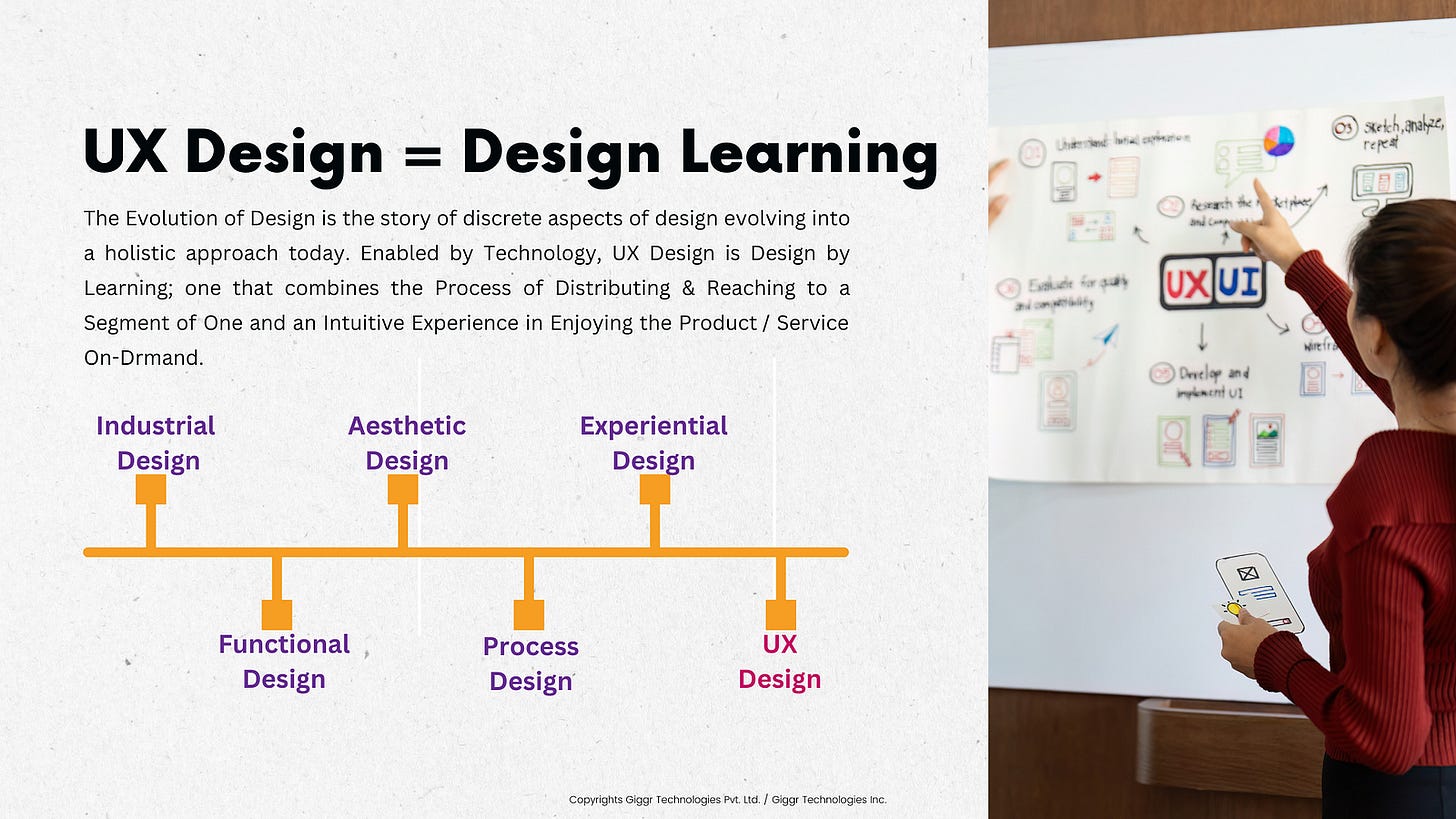
UX is the new Learning Tool
User Experience (UX) refers to a User’s emotions and attitudes when using a product, system, or service. It includes feasibility, usability, accessibility, performance, design, utility, and overall human interaction. Don Norman, who coined the term when he was at Apple, emphasized that UX goes beyond the interface; it includes all aspects of the user’s interaction with the company, its services, and its products. Shouldn’t this be the best tool to learn and design for what Customers and Consumers love?
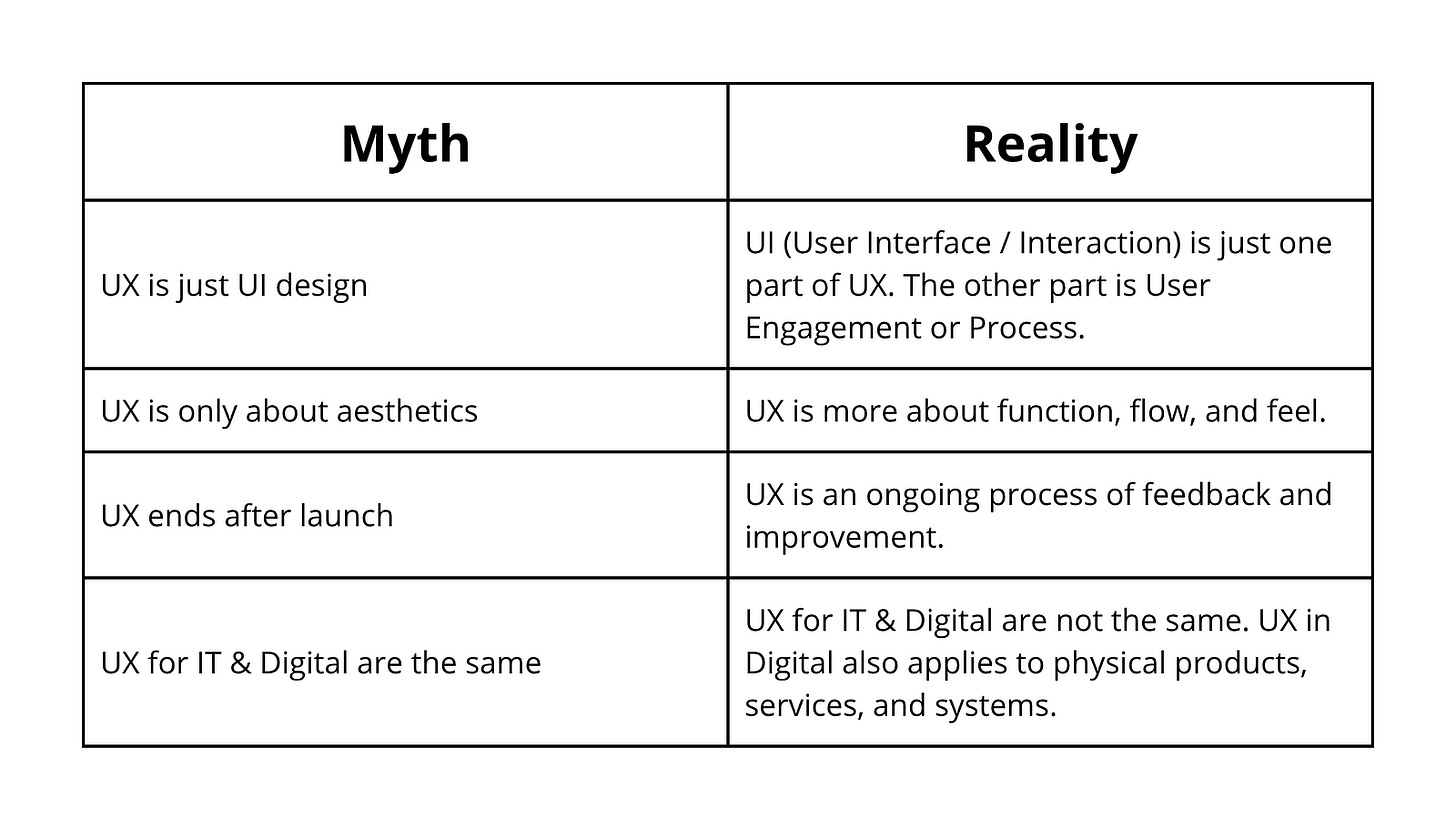
What UX Is Not (But Often Confused With)
Learning by Design
The journey of strategy as a value creation discipline represents one of the most significant intellectual developments in business thinking over the past six decades. This evolution reflects changing economic conditions, technological advances, and evolving understanding of how organizations create and capture value.
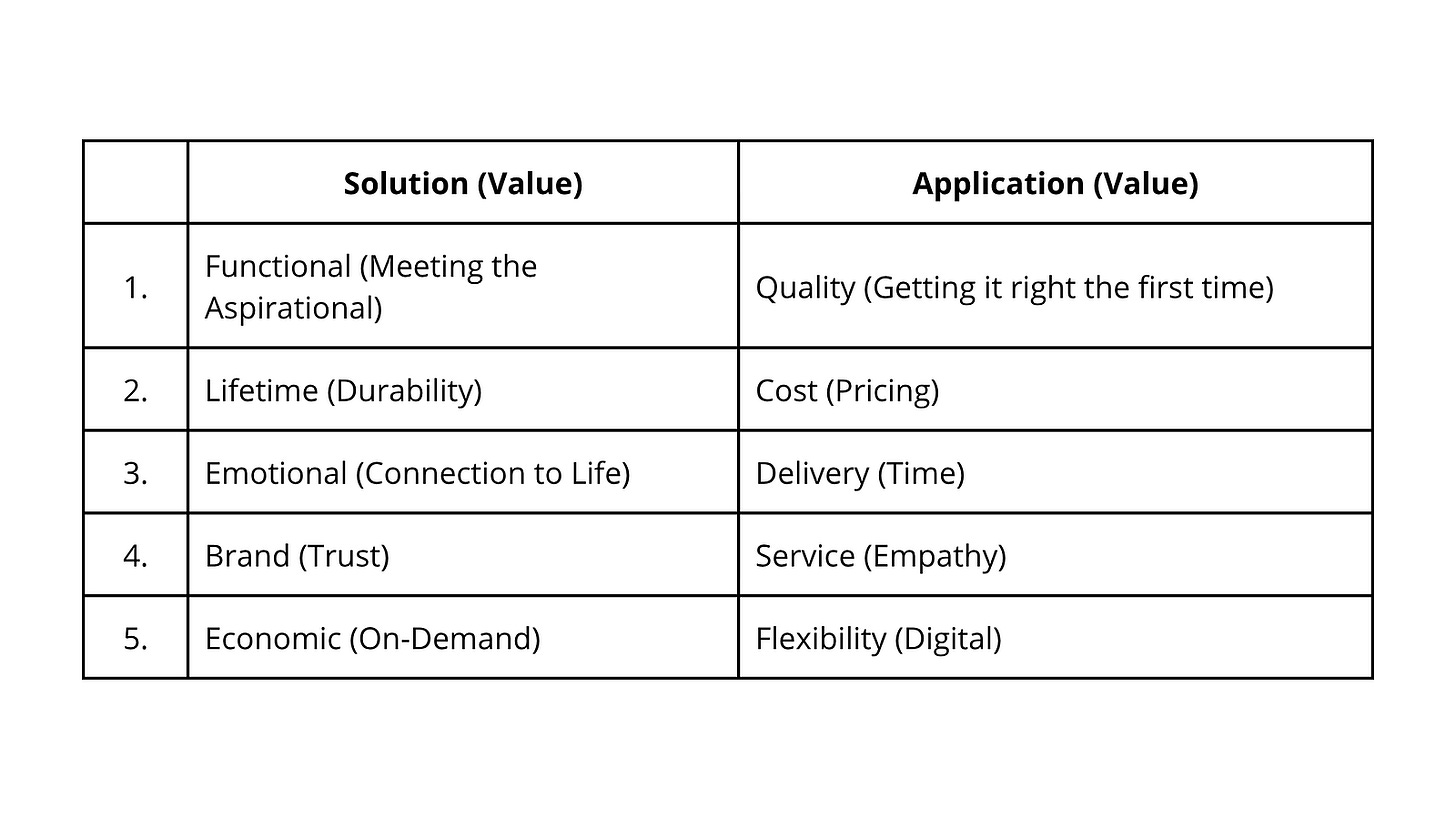
Learning is the foundation on which the future will be built. UX (User Experience) is conventionally interpreted as the overall experience a user has when interacting with a product, service, or system, especially in terms of how easy, intuitive, efficient, and satisfying that interaction is. It has to fulfill five conditions of Value at a Solutions Level as well as five Conditions at an Applications Level, as the following Table illustrates:
Engaging actively with customers and consumers through digital user experience is essential for enriching a design playbook that ensures system efficacy, connecting potential (intent) with performance (impact). This suggests that innovation is not merely an abstract idea but a structured journey that progresses from simplifying processes to modernizing technology and ultimately disrupting business models. Design should fulfill the objectives of learning and educating, adapting through ownership and commitment, and promoting institutionalization.
The shift from industrial to intelligent strategy represents more than a technological upgrade; it’s a fundamental evolution in how human organizations create, capture, and distribute value. Success in the intelligent era requires mastering the integration of human wisdom with machine intelligence, creating adaptive strategic systems capable of thriving in an era of Exponential Transformation and Unprecedented Potent.
The future belongs to those who understand that the highest form of fitness is the ability to create conditions where everyone in the ecosystem can thrive.